Google Sheets API Limits, What It Is and How to Avoid It
Google Sheets is one of the most popular products from Google. It's part of the popular G Suite, which includes other tools like Google Docs, Google Forms, Google Slides, and Google Drive. They're all saved in the cloud, so they can be accessed from anywhere.
Most of these services are similar to the Microsoft Office tools like Microsoft Word and Excel. But what makes them popular is that they're free and don't change like Microsoft Office. They're also not tied to a computer since they're saved on the cloud.
Google provides an awesome API service for Google Sheets. With version 4, which was released in 2016, we can now complete all tasks in the same place. Earlier, we were limited to only reading and writing in cells, but now we can filter views, create tables, and do all sorts of other tasks.
In this post, we'll learn about the Google Sheets API limits. When we're making a production app, using Google Sheets as a back end to store data, we often hit this rate limit. So, let's see what that limit is and how we can avoid it.
The first question that will come to mind for anyone deciding to use Google Sheets API is wheter it's **free to use**
Is Using Google Sheets API Free?
The first question that will come to mind for anyone deciding to use Google Sheets API is whether it's free to use.
Yes, it's completely free to use, but it has a quota assigned to it. This quota has been assigned to safeguard Google APIs from hackers. These hackers hit API endpoints with a lot of traffic to bring it down.
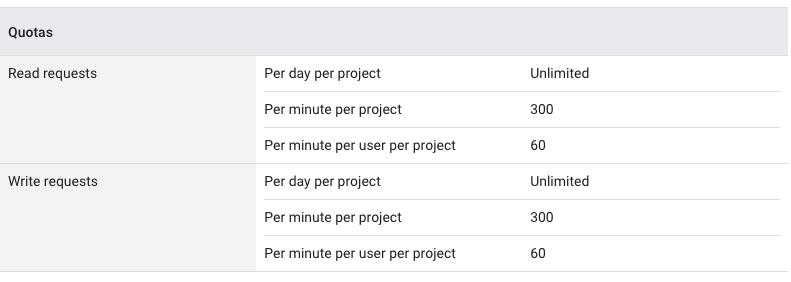
As per the documentation, there's a **limit** on **per minute per project**
What Is the Limit for Google Sheets API?
Now, the next question concerns the limit for Google Sheets API. The rate limit of Google Sheets API is shown below. The official documents can be referenced here. As per the documentation, there's a limit on per minute per project.
We can see that with per day per project we get unlimited read and write requests.
Exceeding a Quota
In bigger production applications, you'll be making an API call from the same service account with the same user. So, in those cases, you'll often exceed the rate limit of 60. If the quota limit is exceeded, we'll get the error code 429: Too many requests.
In this scenario, we should use an exponential backoff algorithm, as suggested in the official documentation here. In the exponential backoff algorithm, we need to write code that catches the exceptions. After it catches the exception, it has to retry.
Now, if the API request fails again, the program needs to try again after increasing the request time. If it fails another time, then we increase the API request time and try again. We'll need to keep on increasing the time and try until we succeed.
Exponential Backoff Algorithm Implementation
Below is the implementation of the same that has been done in Node.js. You can find all other implementations in all major languages here.
Now, we need to give our Google cloud storage bucket and ID first. After that, import the main function of storage from Google.
Then, create a new instance of storage and pass an object to it. This object contains some important parameters required by the storage class. These parameters are
- autoRetry—This needs to be set to true for retry to happen.
- retryDelayMultiplier—This is the multiplier that increases the delay time after every failed request.
- totalTimeout—This represents the time between an initial request and its timeout.
- maxRetryDelay—This is the maximum delay allowed. After this is reached, the retryDelayMultiplier won't be used.
- maxRetries—This is the maximum number of retries allowed.
- idempotencyStrategy—This tells which kind of operation we have. If it's set to RetryAlways, it'll follow all the options above.
const bucketName = 'your-unique-bucket-name';
const fileName = 'your-file-name';
const {Storage} = require('@google-cloud/storage');
const storage = new Storage({
retryOptions: {
autoRetry: true,
retryDelayMultiplier: 3,
totalTimeout: 500,
maxRetryDelay: 60,
maxRetries: 5,
idempotencyStrategy: IdempotencyStrategy.RetryAlways,
},
});
console.log(
'Functions are customized to be retried according to the following parameters:'
);
console.log(`Auto Retry: ${storage.retryOptions.autoRetry}`);
console.log(
`Retry delay multiplier: ${storage.retryOptions.retryDelayMultiplier}`
);
console.log(`Total timeout: ${storage.retryOptions.totalTimeout}`);
console.log(`Maximum retry delay: ${storage.retryOptions.maxRetryDelay}`);
console.log(`Maximum retries: ${storage.retryOptions.maxRetries}`);
console.log(
`Idempotency strategy: ${storage.retryOptions.idempotencyStrategy}`
);
async function deleteFileWithCustomizedRetrySetting() {
await storage.bucket(bucketName).file(fileName).delete();
console.log(`File ${fileName} deleted with a customized retry strategy.`);
}
deleteFileWithCustomizedRetrySetting();
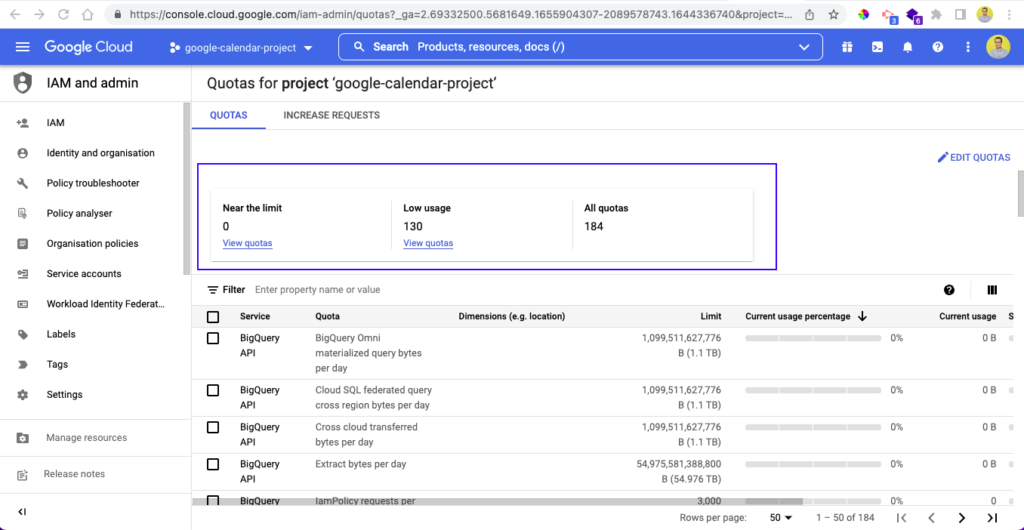
Viewing Quota Limits
You can view your quotas of an app by logging in to the Google cloud console through this link. It'll show the quota of the last working application.
You can also see the INCREASE REQUESTS tab beside the QUOTAS tab. Upon clicking on it, you'll find any increased requests that have been given.
To see a quota limit of a different project, just click on the down arrow of the project. After that, it'll open a pop-up window, where you can click on other projects to see their quota.
How Do I Increase Google Sheets API Limit?
Now, if your limit is reached, then what is the process to increase the Google sheets API limits?
We simply have to apply if we want Google to increase the quota limit. And, as per Google, even if you apply for a quota increase, it doesn't guarantee an increase.
In fact, large quota increases can take a very long time to approve.
When we request a quota increase, an AI system from Google evaluates it. It checks for different factors like how long we've used Google cloud and other things.
In some cases, requests are handled by humans, and they also follow a strict guideline.
If the request is approved, then the user has to pay in advance for the quota increase. Quota increase requests are generally resolved within two to three business days.
We need to give the quota increase request through the Google cloud console. Log in by following the steps listed above. After that, click on the checkbox next to the request noting that you want to increase the quota. Then, click on EDIT QUOTAS toward the top right of the page.
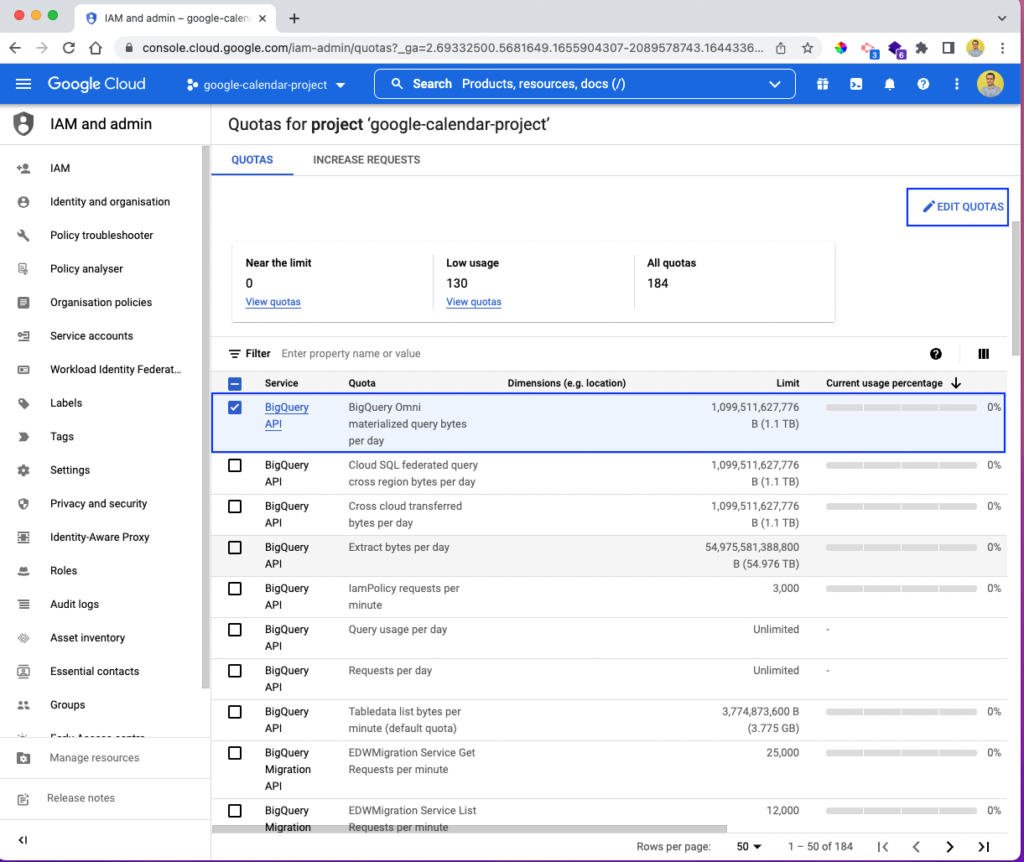
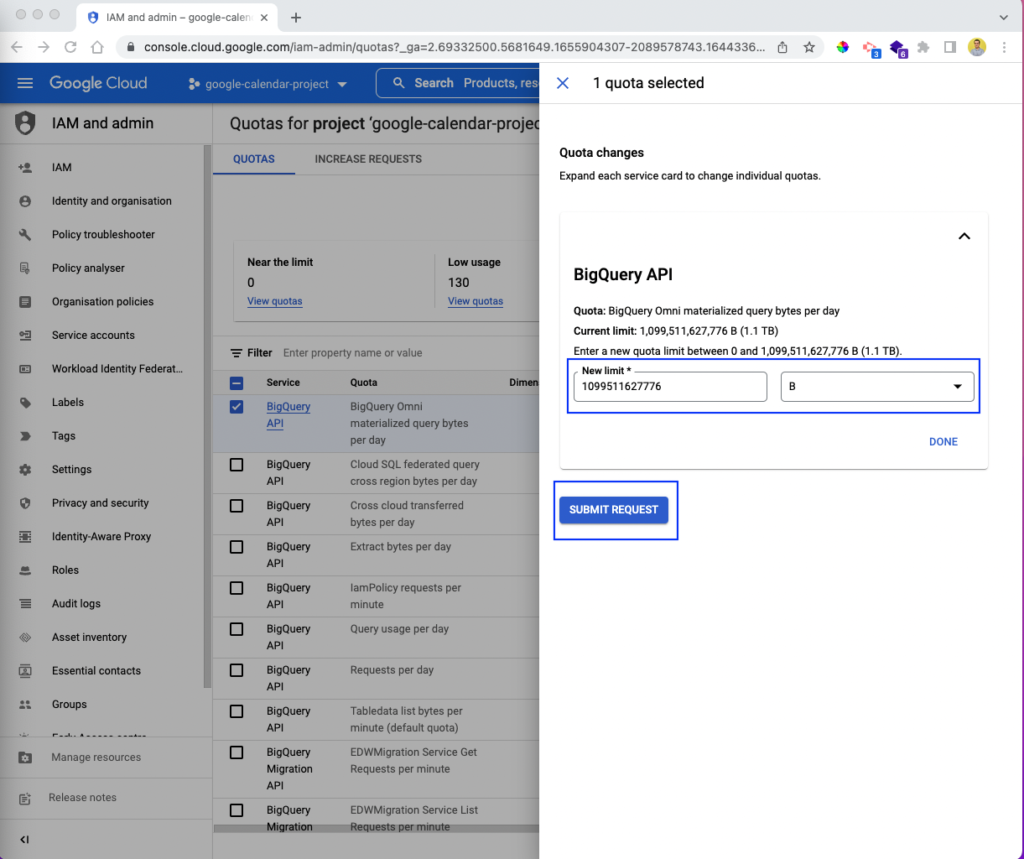
This will open a pop-up window, in which you can update the limit to give a new limit. You'll also see the metrics bytes, kilobytes, megabytes, gigabytes, terabytes, and petabytes. Give the new updated values, and click on the SUBMIT REQUEST button.
Conclusion
In this post, we've learned about rate limit issues in the Google Sheets API. We first briefly learned about Google Sheets and the freely available API with it.
With the help of Google Sheets API, we can do all the usual tasks of reading and writing in a cell. Aside from this, we can also do the advanced task of filtering views and creating tables.
We also learned about the different limits in Google API. Then, we learned what happens when we exceed a quota.
Further, we've seen in detail the exponential backoff algorithm implementation. We've also learned how to view the quota limits in the Google cloud console. Last, we learned how to increase the quota through the Google cloud console. Here, we also learned how Google uses a combination of AI and human operators to approve our quota increase requests.
Before your go..
This post was written by Nabendu Biswas. Nabendu has been working in the software industry for the past 15 years, starting as a C++ developer, then moving on to databases. For the past six years he’s been working as a web-developer working in the JavaScript ecosystem, and developing web-apps in ReactJS, NodeJS, GraphQL. He loves to blog about what he learns and what he’s up to.
