Node.js WebSocket Client: 3 Ways to Implement One
This article will explore the best ways to implement a Node.js WebSocket client. To do this, you'll create your own implementation of a WebSocket server that will establish a connection with your client and feed you with a real-time clock.
First, we'll briefly refresh you on what WebSockets are and why they exist. Then we'll discuss whether Node.js actually supports WebSockets on both the server and client sides. Next, we'll have you create a WebSocket server in Node.js that will accept connections and feed data to clients. Finally, we'll implement a WebSocket client in Node.js and explore alternative ways to achieve the same goal.
As you can see, this article heavily depends on you taking action and coding as we go. So, if you have no experience with Node.js, please get yourself acquainted with it here.
A WebSocket is a protocol that allows participants to mantain and open connection and exchange data freely
What Is a WebSocket?
A WebSocket is a protocol that allows participants to maintain an open connection and exchange data freely.
Commonly, HTTP is the protocol of choice for facilitating communication between a server and a client. And for the most part, it's more than sufficient. However, using HTTP is not always the best course of action, especially when a continuous, bidirectional stream of data is required. In those cases, using WebSockets is the way to go.
WebSockets provide an open connection between the server and the client and two-way communication between the server and the client. Also, it avoids polling the server.
Does Node.js Support WebSockets?
Now, you might be asking yourself, does Node.js support WebSockets? And the simple answer is yes, it does. But for the most part, you will be better served with the native WebSocket implementation in the browser.
As you already know, WebSockets establish and maintain a connection between a client and a server. The client is usually implemented at the user browser and is handled by the native WebSocket implementation in JavaScript. Typical implementations are chat rooms, live boards, and live streaming.
However, there might be some cases where you want to implement a WebSocket solution between a server and another application that doesn't lie in the browser directly. For example, maybe you need to establish an efficient duplex communication channel between two applications. Or perhaps you want a middle layer to handle the output from the server in Node.js. Whatever the case might be, you can implement a WebSocket mechanism with Node.js as the client just the same.
Now let's illustrate how to make this all work with some code.
Creating a WebSocket Server in Node.js
First, you're going to need a server that receives connections and provides some sort of real-time data. You'll use Node.js to create this server, which will feed the current time to the client.
Let’s dive in. You can checkout and run the example application locally via Runme. Otherwise go ahead and follow the tutorial.
Start by creating a Node.js project and adding the following dependencies:
$ npm install --save express
$ npm install --save ws
$ npm install --save bufferutil
$ npm install --save utf-8-validate
For context, 'express' will be your primary webserver middleware to handle the server communication and logic. Additionally, 'ws' is a simple, fast, and tested WebSocket client implementation for Node.js. It will be the primary mechanism to establish connections and serve data to your clients. Lastly, 'bufferutil' and 'utf-8-validate' are libraries that enhance 'ws' performance and security by providing utilities to perform operations such as masking and unmasking data payloads efficiently.
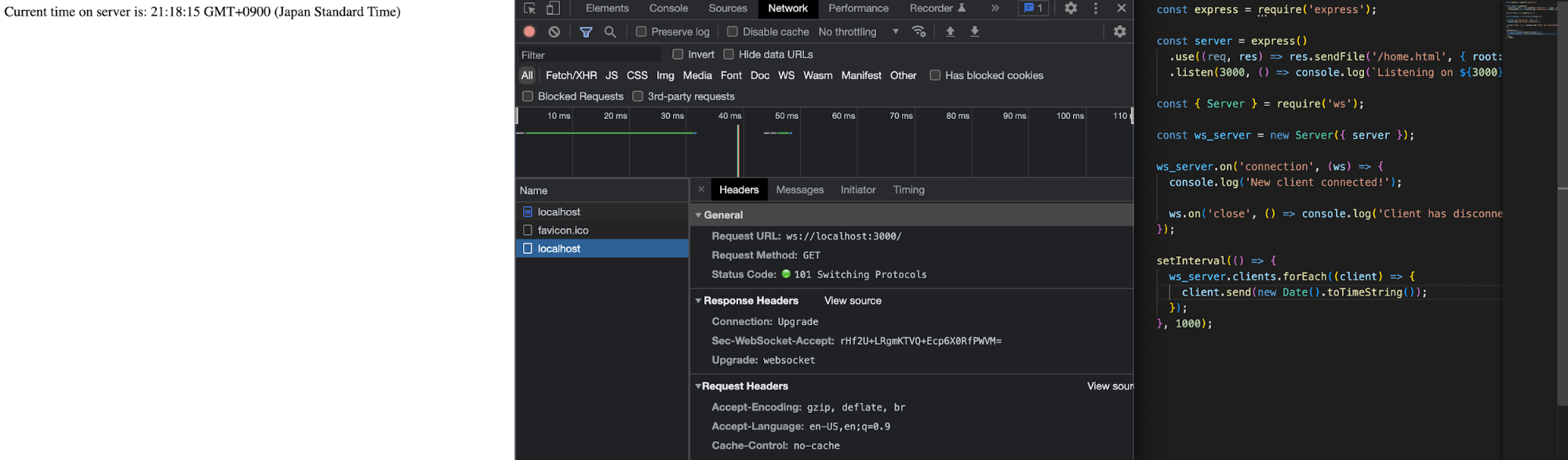
Now create an HTML file and call it home.html. You can keep it blank for now. Then create a basic 'express' server. You will use this to provide a hook for the WebSocket server to monitor for client requests.
The following code is an example of an 'express' server implementation:
const express = require('express');
const server = express()
.use((req, res) => res.sendFile('/home.html', { root: __dirname }))
.listen(3000, () => console.log(`Listening on ${3000}`));
Next is the actual WebSocket server.
First, you must create a new instance of the 'ws' Server and provide an HTTP server as a parameter. This is so that it can listen for connection events.
The most straightforward implementation would be the following:
const { Server } = require('ws');
const ws_server = new Server({ server });
Good.
Now you need to provide the handling mechanism for WebSocket connections. This is pretty simple since all you have to do is listen for connection events and make sure you handle disconnections.
Here's a basic example:
ws_server.on('connection', (ws) => {
console.log('New client connected!');
ws.on('close', () => console.log('Client has disconnected!'));
});
Notice that this implementation closely follows standard JavaScript event handling mechanisms.
Finally, add the logic to send updates to the client every one second. You can pass a simple date string with the server's current date and time so the client can consume it.
setInterval(() => {
ws_server.clients.forEach((client) => {
client.send(new Date().toTimeString());
});
}, 1000);
And that's it.
You can go ahead and run it, but it won't do much yet without a client. So now let's move on to the client.
How to Implement a WebSocket Client in Node.js
Alright, before you implement a WebSocket client in Node.js, we want to ensure that things are working just fine, so let's create a rudimentary browser client within an HTML file.
All you have to do is update the home.html file and add the following code:
<html>
<head>
<script>
let webSocket = new WebSocket(location.origin.replace(/^http/, 'ws'));
let el;
webSocket.onmessage = (event) => {
el = document.getElementById('time');
el.innerHTML = 'Current time on server is: ' + event.data;
};
</script>
</head>
<body>
<p id="time"></p>
</body>
</html>
Notice that we're using the native WebSocket implementation in JavaScript. As we have mentioned, this is how most WebSocket clients are implemented.
Checkout the full example locally via Runme.
Using websocket-node
To implement the WebSocket client on Node.js, you can use one of the many package libraries available. One of the simplest is 'websocket-node,' a pure JavaScript implementation of the WebSocket protocol for Node. Much like the implementation of the server, the client will use the standard event-driven mechanism to establish and handle communication with the server.
Here's an example that accomplishes the same result.
const WebSocketClient = require('websocket').client;
var client = new WebSocketClient();
client.on('connectFailed', function(error) {
console.log('Connect Error: ' + error.toString());
});
client.on('connect', function(connection) {
console.log('Connection established!');
connection.on('error', function(error) {
console.log("Connection error: " + error.toString());
});
connection.on('close', function() {
console.log('Connection closed!');
});
connection.on('message', function(message) {
console.log("Current time on server is: '" + message.utf8Data + "'");
});
});
client.connect('ws://localhost:3000/', 'server time');
Notice that you have a few more handling events in this example. These are not necessary, but they are more verbose and help diagnose and maintain a more reliable connection.
This package is a general-purpose WebSocket implementation extracted from the Faye project that provides classes for quickly building WebSocket servers and clients in Node
Checkout the full example locally via Runme.
Using faye-websocket-node Package
You can also create a WebSocket client in Node with the 'faye-websocket-node' package. This package is a general-purpose WebSocket implementation extracted from the Faye project that provides classes for quickly building WebSocket servers and clients in Node.
A simple implementation of this package would look like the following:
var WebSocket = require('faye-websocket');
var client = new WebSocket.Client('ws://localhost:3000/');
client.on('open', function(message) {
console.log('Connection established!');
});
client.on('message', function(message) {
console.log("Current time on server is: '" + message.data + "'");
});
client.on('close', function(message) {
console.log('Connection closed!', message.code, message.reason);
client = null;
});
Checkout the full example locally via Runme.
Using the sockette Package Library
One last implementation of the WebSocket client in Node.js that you can use is the 'sockette' package library.
Sockette is a thin wrapper around the WebSocket native library that automatically reconnects if the connection is lost. Additionally, Sockette allows you to reuse your instances, avoiding the need to redeclare event listeners.
An implementation of the Sockette library would look like the following:
const Sockette = require('sockette');
const client = new Sockette('ws://localhost:3000', {
timeout: 5e3,
maxAttempts: 10,
onopen: message => console.log('Connection established!', message),
onmessage: message => console.log("Current time on server is: '" + message.data + "'"),
onreconnect: message => console.log('Reconnecting...', e),
onmaximum: message => console.log('Connection failed!', e),
onclose: message => console.log('Connection closed!', message.code, message.reason),
onerror: error => console.log("Connection error: " + error.toString())
});
client.send('Tell me the time!');
client.json({type: 'ping'});
client.close(); // graceful shutdown
// Reconnect 10s later
setTimeout(ws.reconnect, 10e3);
As you can see, the implementation is similar across the multiple package libraries.
One of the most critical aspects of service development is implementing a robust and reliable communication mechanism for its clients
Checkout the full example locally via Runme.
In Conclusion
One of the most critical aspects of service development is implementing a robust and reliable communication mechanism for its clients. Depending on the instrument of choice and the goal, you could end up making or breaking the whole thing. That's why making the right choice from the beginning is vital. With all these examples, we hope that you have the right tools to create a solid and reliable service for your clients.
This post was written by Juan Reyes. Juan is an engineer by profession and a dreamer by heart who crossed the seas to reach Japan following the promise of opportunity and challenge. While trying to find himself and build a meaningful life in the east, Juan borrows wisdom from his experiences as an entrepreneur, artist, hustler, father figure, husband, and friend to start writing about passion, meaning, self-development, leadership, relationships, and mental health. His many years of struggle and self-discovery have inspired him and drive to embark on a journey for wisdom.
